STDs (Sexually Transmitted Diseases), i.e. sexually transmitted diseases, can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. Patients' complaints are usually expressed in the form of urethral or vaginal discharge, burning sensation when urinating, itching in the genital region, painful intercourse, and lower abdominal discomfort. Sexually transmitted infections are often symptomless or have mild symptoms, so it is extremely important to perform an STD screening and carry out the therapy recommended by the doctor. Contact one of our 9 highly qualified gynecologists working at our clinics in Buda and Pest to avoid the serious consequences of sexually transmitted diseases, such as impotence, infertility, and cancer symptoms.
"Don't delay the screening, because in many cases it can be asymptomatic!"

STD tests and screening for sexually transmitted pathogens for symptomatic and asymptomatic patients
STDs, i.e. sexually transmitted diseases, can also be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. Patients' complaints are usually expressed in the form of urethral or vaginal discharge, burning sensation when urinating, itching in the genital region, painful intercourse, and lower abdominal discomfort. In most cases, the symptoms noticed by the patient are not specific to a particular pathogen.
In the case of which complaints is STD testing or screening recommended?
- Flow (for men, discharge from the urethra or discharge from the rectum, for women, vaginal discharge)
- Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae canter/tripper (secretion dripping from the urethra, increased vaginal discharge)
- Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydiasis (inflammation of the cervix, inflammation of the urethra, increased discharge, lower abdominal pain)
- Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis LGV (lymphogranuloma venereum) - discharge from the rectum, mainly after anal sex
After/in addition to the exclusion of the above classical sexually transmitted pathogens, the presence of the following "atypical" bacteria may arise.
- Inflammation of the urethra caused by Mycoplasma genitalium, discharge in women (often asymptomatic)
- Inflammation of the urethra and cervix caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum
However, it is important to note that it is located in the vagina Disturbance of the balance of Lactobacillus flora can also cause more vaginal discharge. In such cases, it is not a venereal disease, but the defense mechanism of the vagina is damaged, so restoration of flora is definitely recommended, especially to prevent the proliferation of sexually transmitted pathogens.
Itching, red spots:
- inflammation caused by fungi (Candida species).
Wart on the genitals or in the genital region:
- Genital warts and condylomas caused by HPV
- other viral warts, e.g. molloscum contagiosum (small warts with a navel-like indentation in the middle)
Wound, ulcer on the genitals or genital region (even in the mouth or rectum):
- Syphilis – Treponema pallidum
- Genital herpes – both HSV-2 and HSV-1
- Cervical cancer, penile cancer, rectal cancer caused by HPV
- Strange, non-healing skin symptoms, fever, fever, enlarged lymph nodes
- HIV infection caused by the HIV virus, AIDS in advanced cases
Sexually transmitted diseases also include viral hepatitis caused by Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C (in the case of anal sex, Hepatitis A infection can also be classified here).
What if you are asymptomatic?
Sexually transmitted infections are often symptomless or have mild symptoms, so it is extremely important to perform an STD screening. The lack of appropriate treatment can lead to serious complications for the patient and his partner, infertility, impotence, and in some cases even the development of tumors.
When and for whom is screening recommended?
- In the case of a new partnership, in this case it is advisable to have the screening done before the first sexual intercourse.
- Screening is recommended for both members of the couple, preferably at about the same time, even if the female partner regularly attends gynecological examinations. (Screening for STD pathogens is not part of the routine gynecological examination)
- If you have several partners at the same time or frequently change partners.
- Family planning, before having children for both members of the couple.
How and where is the sampling done?
Blood test HIV infection, syphilis and viral liver inflammation (Hepatitis B, C) can be detected. We also use a blood test to show whether the patient has ever experienced, e.g. herpes virus infection.
From the urethra the causative agents of urethritis can be confirmed from a small, sterile cotton swab sample (Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum).
For women from vagina or from the mouth of the bee we take a sample.
In case of wound a from the wound surface we take a sample with a sterile cotton swab.
In case of warts a from the surface of the wart a sample is taken with a sterile cotton swab in order to isolate or exclude the HPV virus.
Can treatment cure the infection?
In the case of a proven pathogen, the treating physician prescribes antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals based on professional guidelines. All of the bacteria that cause STDs can be cured with antibiotics taken in the right dose and for the right amount of time. This is determined by medical competence.
Fortunately, HIV infection can also be treated these days. By taking appropriate antiviral drugs regularly and for life, the infectivity of an infected person can be reduced to zero. Initiating and controlling treatment against HIV is the competence of an infectious disease specialist.
In the case of a herpes virus infection, the patient receives antiviral treatment, which unfortunately does not mean a permanent cure in some cases, recurrence can be expected.
HPV infection is fought by the immune system itself, but by administering the vaccine, the patient can prevent the possibility of repeated infection. Warts caused by HPV can be removed most quickly with laser treatment, the effect of which is immediate. Brushing warts with an antiviral solution or local freezing can be another solution.
When and who can get the HPV vaccine?
We recommend the HPV vaccine to all our patients, regardless of age, gender or HPV status. This means that even those with previously known HPV positivity can receive the vaccine. Vaccination is not a cure for an existing infection (it is eliminated by the immune system, warts can be frozen, brushed with an antiviral solution or removed with laser treatment), however, once the series of vaccinations is completed, the patient will not be infected again with the HPV virus in the future.
Our related articles

Treatment of the HPV virus

Genital warts: their symptoms and treatment
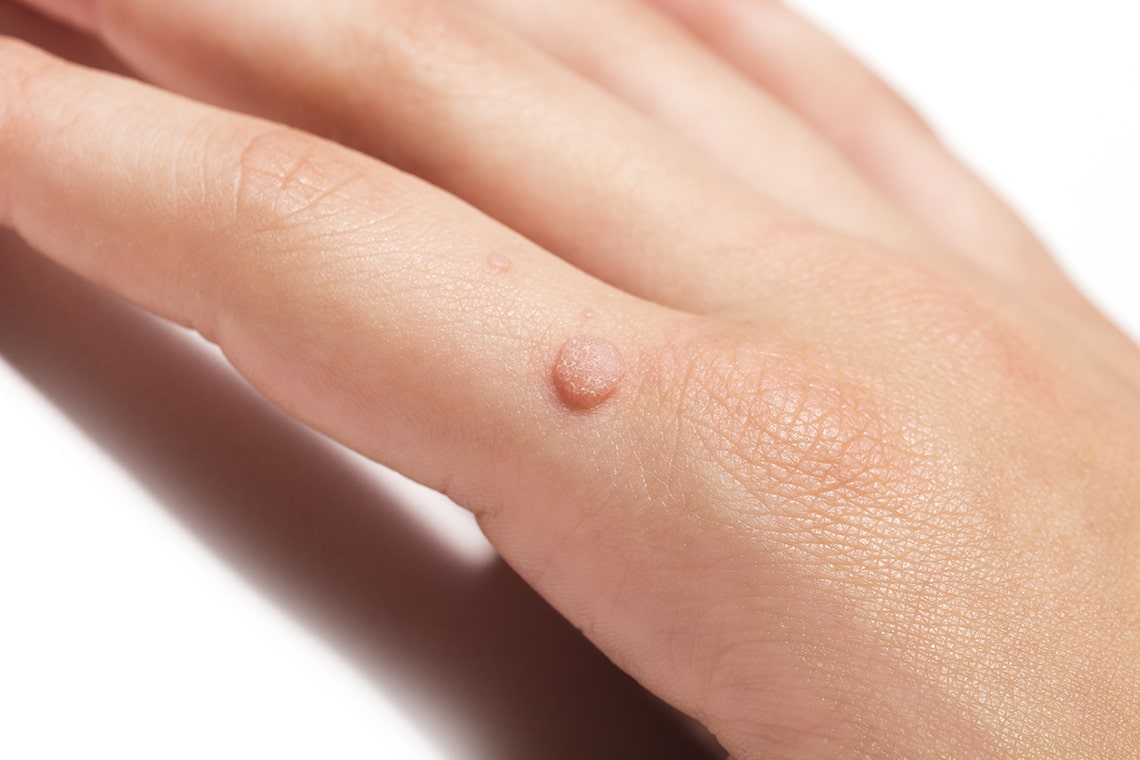
Laser wart removal
Our doctors
Our prices
- NON-DRUG MEDICINE / STD CONSULTATION AND EXAMINATION, CONTROL EXAMINATION
- Specialist examination, consultation: 32.000 - 34.000 HUF
- Leading specialist medical examination, consultation: 34.000 - 36.000 HUF
- Online consultation: HUF 20.000
- Online control: HUF 14.000
- NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENTS AND INTERVENTIONS
- Laser removal of warts, skin growths, and fibroids (the price varies depending on the size and number of pieces and includes the consultation and anesthesia fee)
- Under 1 cm, 1 piece: HUF 38.000 (includes consultation and anesthesia fees)
- Under 1 cm, 2-3 pieces: HUF 43.000
- Under 1 cm, 4-6 pieces: HUF 49.000
- Under 1 cm, 7-10 pieces: HUF 53.000
- Under 1 cm, 11-15 pieces: HUF 62.000
- Under 1 cm, 16-20 pieces: HUF 74.000
- Under 1 cm, over 21 pieces: HUF 86.000
- 1-2 cm in size, 1 pc.: HUF 40.000
- 1-2 cm in size, 2-3 pieces: HUF 45.000
- 1-2 cm in size, 4-6 pieces: HUF 55.000
- 1-2 cm in size, from 7 pieces: From HUF 68.000
- Larger than 2 cm, 1 pc.: HUF 43.000
- Larger than 2 cm, 2-3 pcs.: HUF 50.000
- Larger than 2 cm, 4-6 pcs.: HUF 62.000
- More than 2 cm, more than 7 pieces: From HUF 81.000
- STD LAB TESTS
- Please note that laboratory tests are payable in addition to the specialist consultation and examination fees.
- Herpes simplex virus (1/2) by PCR genotyping: HUF 9.000
- Herpes simplex virus, Type 1,2, IGG, IGM: HUF 15.000
- Hepatitis B antigen: HUF 10.000
- HIV 1,2: HUF 10.000
- HPV detection and typing: HUF 16.000
- PCR tests: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma genitalium, Trichomonas vaginalis, Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, Treponema pallidum: HUF 9.000/ pathogen
- Panel 2 (Treponema pallidum, Herpes simplex virus 1/2): HUF 14.000
- Panel 3 (Trichomonas vaginalis, Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae): HUF 17.000
- Panel 4 (Chlamydia, Mycoplasma, Ureaplasma, Neisseria gonorrhoeae): HUF 21.000
- Bacterial culture and resistance test (aerobic): HUF 10.000
- Bacterial culture (aerobic and anaerobic): HUF 22.000
- Bacteria culture (aerobic) + germinating fungus: HUF 11.500












